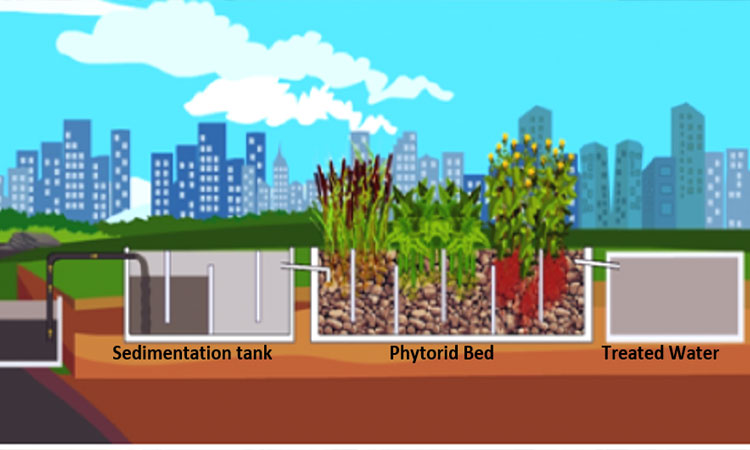
The purpose of this Development Role Manual for Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) [SBM (G)] is to create an enabling mechanism for improved implementation of the Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) at the cutting edge, leading to enhanced outcomes in nature and extent. Accordingly, it would act as a guide for implementation by the District Collector and key District-level functionaries, enable quick learning, implementation modalities, roles and responsibilities of the various functionaries as well as stakeholders etc.